What Is Thymic Hyperplasia?
Thymic hyperplasia refers to an enlargement or overgrowth of the thymus gland. The thymus is a small organ located in the chest, behind the sternum and in front of the heart. It plays a crucial role in the development and maturation of certain immune cells called T lymphocytes or T cells, which are important for the proper functioning of the immune system.
Thymic hyperplasia means that the thymus gland remains enlarged or grows in size beyond what is normal for age. It is usually benign, but can sometimes be difficult to differentiate from thymoma, which is a thymic tumor or growth. Thymic hyperplasia is usually asymptomatic but can sometimes cause chest pain, cough, or shortness of breath depending on the size of the enlarged gland.
Causes Of Thymic Hyperplasia.
A. Persistence of thymic tissue after puberty:- The thymus gland fails to undergo normal age-related atrophy and remains enlarged.
B. Rebound thymic hyperplasia:- After chemotherapy or immunosuppression, the thymus gland enlarges again during immune recovery.
C. Stress or illness :- Conditions like sepsis, burns, surgery can stimulate the thymus to temporarily enlarge.
D. Autoimmune conditions :- Diseases like myasthenia gravis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc. can be associated with thymic hyperplasia.
E. Infections :- Viral infections such as HIV, Epstein-Barr virus, etc. have been linked to thymic hyperplasia.
F. Hormonal factors:- Some endocrine disorders, such as Graves’ disease (an autoimmune disorder affecting the thyroid gland) or thymoma (a tumor originating from the thymus), can lead to thymic hyperplasia.
Symptoms Of Thymic Hyperplasia.
Thymic hyperplasia often does not cause any specific symptoms and is commonly discovered incidentally during imaging studies. However, in some cases, depending on the underlying cause and the extent of enlargement, thymic hyperplasia may be associated with certain symptoms. These can include:-
A. Chest pain:- The enlarged thymus gland can cause pain or pressure in the chest. The pain is usually worse with movement or deep breathing.
B. Cough:- The enlarged thymus can irritate the phrenic nerve which supplies the diaphragm, leading to a chronic cough.
C. Shortness of breath:- Due to pressure from the enlarged thymus, patients may experience difficulty breathing or unable to take deep breaths.
D. Fatigue:- Some patients report feeling tired or having low energy due to the body’s increased efforts to support the enlarged gland.
E. Swollen lymph nodes:- The enlarged thymus gland can stimulate surrounding lymph nodes to swell in some cases.
F. Mediastinal widening:- Chest x-ray may show widening of the mediastinum due to the enlarged thymus gland. This is often an incidental finding.
G. B symptoms:- Rarely, patients may experience fever, night sweats, and unintentional weight loss. This can indicate a more serious underlying condition and needs further evaluation.
H. Compression of adjacent structures:- In severe cases, the enlarged thymus can compress nearby tissues like the superior vena cava, pulmonary artery, phrenic nerve, etc. leading to additional symptoms. This is known as mediastinal thymic hyperplasia syndrome.
I. Hypogammaglobulinemia:- Some patients may have low levels of certain antibodies, known as hypogammaglobulinemia. This can increase the risk of infections.
J. Myasthenia gravis:- In some cases, thymic hyperplasia may be associated with the autoimmune condition myasthenia gravis. Symptoms like muscle weakness may then predominate.
Diagnosis of Thymus Hyperplasia.
The diagnosis of thymic hyperplasia involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and various imaging studies. Here are the commonly used diagnostic approaches:-
A. Laboratory studies:- Acetylcholine receptor antibodies may be positive in some patients with thymic hyperplasia, pointing towards the presence of myasthenia gravis.
B. Imaging:- The thymic hyperplasia is usually discovered incidentally on radiographical imaging for pre-op of some elective surgery or unrelated chest complaints. The findings of a chest radiograph can range from subtle mediastinal findings to large mass or widened mediastinum.
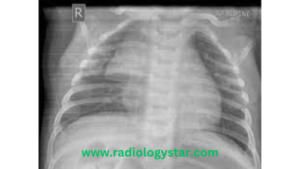
C. Chest X-Ray:- A frontal chest X-ray of infants and young children show a strikingly large thymus and a sail sign can be seen. The thymus normally remains visible on the radiograph till the age of 3 years. On conventional radiography, thymic hyperplasia usually appears normal.
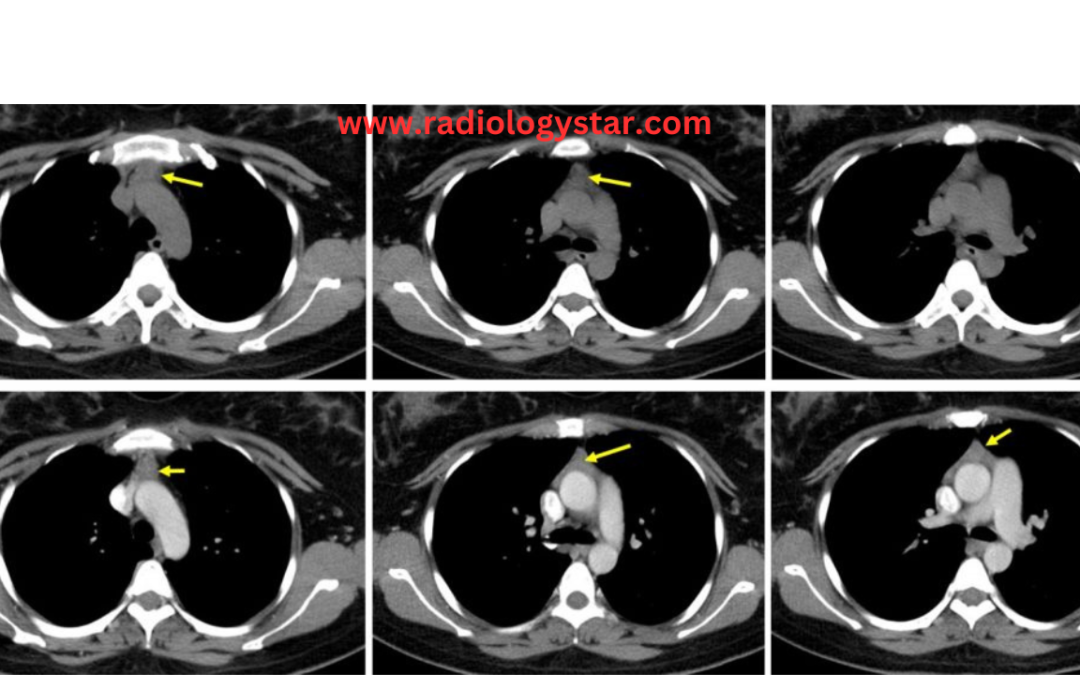
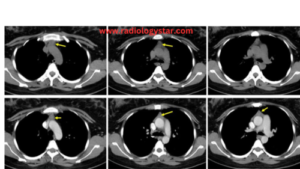
D. Chest CT-scan:- Contrast-enhanced computed tomography is typically used for thymic abnormalities not detected on conventional radiography. In most cases, chest CT-scan is diagnostic. Chest CT-scan can provide comprehensive information about mediastinal abnormality, inclusive of its location, size, relation to surrounding structures, and it can also give you information about the presence of fluid, fat, or calcifications within the tissue. CT-scan of a hyperplastic thymus exhibits diffuse enlargement, preserved contour, normal blood vessels, and a mixture of lymphoid tissue and fat. This precise information is important, especially involvement or compression of related structures in order to plan treatment or resection in severe cases.
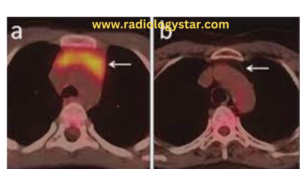
E. PET-CT:- A hyperplastic thymus demonstrates only mild uptake of fluorodeoxyglucose as compared to marked uptake in case of malignancy.
F. Chest MRI:- Chemical shift MRI usually demonstrates chemical shift artifact between in-phase and out of phase images and can help differentiate thymic hyperplasia from thymic neoplasia. It can be challenging to differentiate between normal and hyperplastic thymus; so following guidelines should be used to identify a normal thymus:
— Soft tissue mass should not be greater than 7mm.
— The contour of thymus should not be convex in a young adult.
— Soft tissue must not be ovulated.

G. Biopsy:- In the case of true thymic hyperplasia, the cortex and medulla are normal. Thymic cells are normal on FNA. Lymphofollicular hyperplasia has normal lymphoid follicles with additional germinal centers, dispersed thymic cells, and a few macrophages.
Treatment Of Thymic Hyperplasia.
The some Treatment of thymic hyperplasia options are given below
A. Corticosteroids:- Oral corticosteroids such as prednisone may help shrink an enlarged thymus. This is often used for moderate symptoms. The steroids work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system.
B. Thymectomy:- Surgical removal of part or all of the thymus gland. This is usually only done for severe or persistent symptoms, or if there are complications like airway obstruction or superior vena cava syndrome. Thymectomy results in permanent reduction of the thymus size.
C. Radiotherapy:- Targeted radiation therapy can be used to shrink an enlarged thymus. This is also typically only used for persistent or severe cases where other options have failed or are not appropriate. Radiation works by damaging the thymus cells, causing the gland to shrink over time.
D. Chemotherapy:- Chemotherapeutic drugs that target rapidly dividing cells can be used to reduce thymus size. Like the other options, this is usually only used for severe or refractory cases. The chemotherapy works by killing the thymus cells, causing the gland to shrink.
E. Observation:- For most infants and children with mild to moderate thymus enlargement without significant symptoms, observation is appropriate. The thymus usually naturally shrinks in size over the first few years of life as the immune system develops. So no treatment may be needed, just monitoring.
FOR MORE ARTICLES CLICK HERE
BOOK LINK :- Radiographic Pathology for Technologists